What is RVI?
RVI is the application of remote visualization technologies and processes to the inspection, certification, auditing, and diagnosis of building design, operation, or performance.
RVI has been used for some years but gained increased popularity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Now, many organizations are using some variation of RVI as a tool to reduce the costs of all types of inspection or quality assurance activities that would normally involve a trained professional traveling to a building site. For example, building inspectors in a local jurisdiction may use phone or tablet video inspection, photos, or even drones to inspect the installation of building or energy code measures in a home. Building managers, operators, or contractors can connect with a building automation system (BAS) to evaluate building operations and troubleshoot problems.
Key Steps to RVI
In the context of building codes, Authorities Having Jurisdiction (AHJs) are ultimately responsible for the development of an RVI program and the process by which it will be implemented in the field. Although RVI is still an emerging practice, guidance and resources have been developed to support jurisdictions in this development.
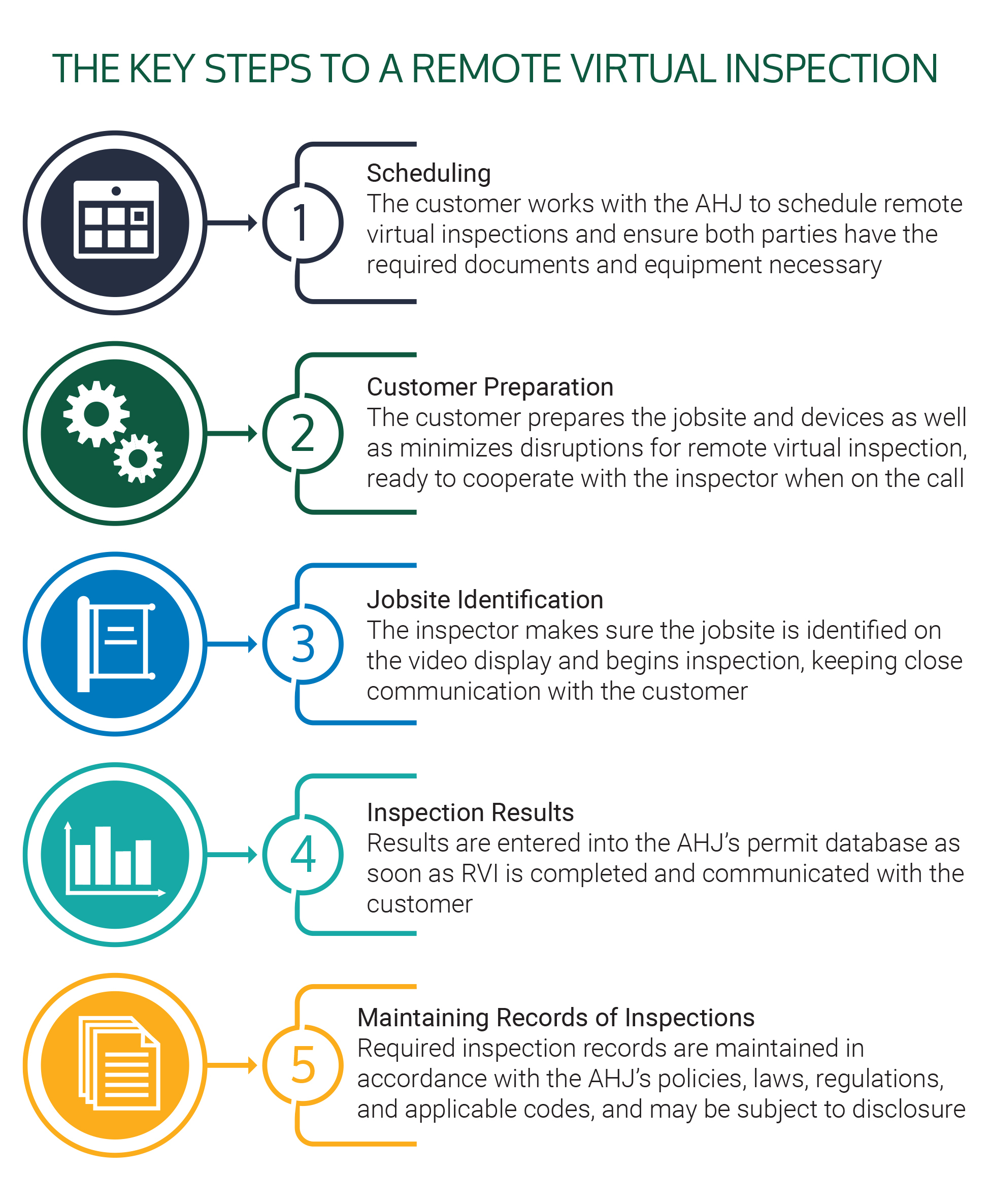
The International Code Council (ICC) developed the above flow chart to provide a high-level outline of how the RVI process may be implemented at the jurisdictional level. This graphic is an introduction to the resource, Recommended Practices for Remote Virtual Inspections (RVI), which provides helpful guidance to AHJs as they develop and implement an RVI program.
BECP RVI Efforts
DOE’s BECP collaborated with ICC on the development and demonstration of a protocol for remote inspection of the residential provisions of the 2018 and 2021 editions of the International Energy Conservation Code.
